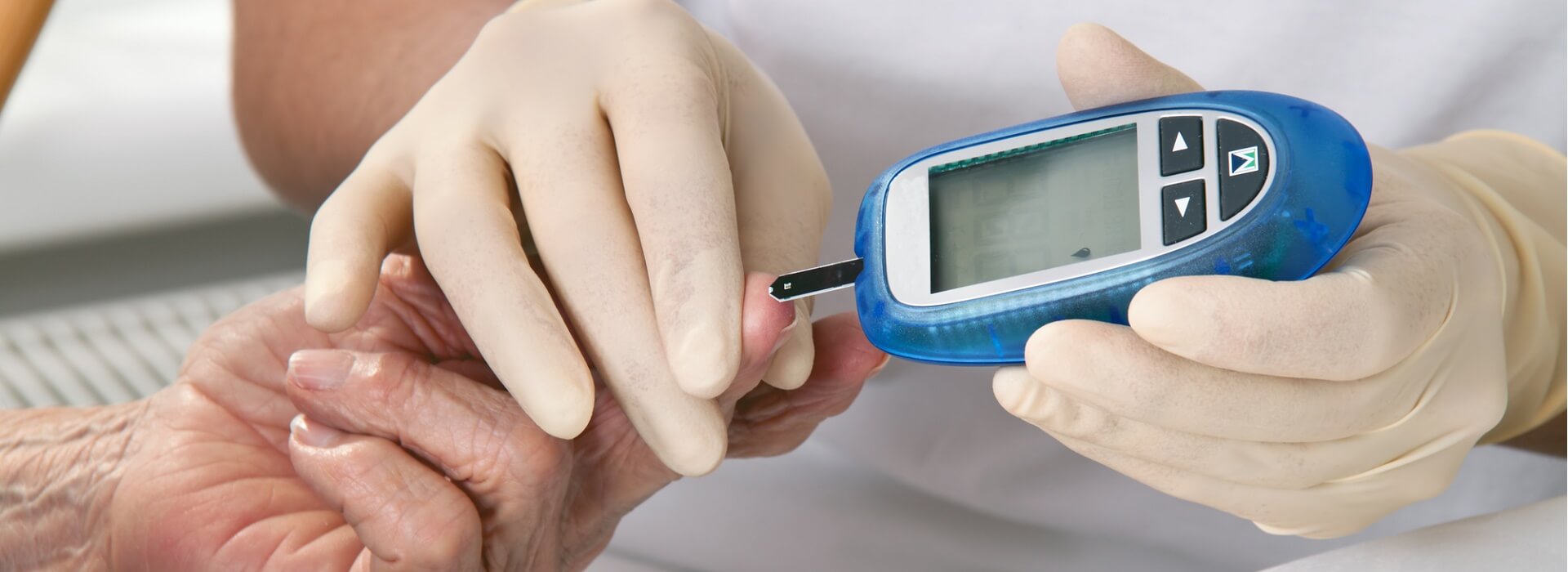
Diabetes mellitus (DM), commonly known as just diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death.
Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced.There are two main types of diabetes mellitusmellitus.
Type 1 diabetes results from failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin due to loss of beta cells. It is also known as "insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus" (IDDM) or "juvenile diabetes".
Type 2 diabetes begins with insulin resistance, a condition in which cells fail to respond to insulin properly. As the disease progresses, a lack of insulin may also develop. It is also known as "non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus" (NIDDM) or "adult-onset diabetes".
Diabetes insipidus - A disorder of salt and water metabolism marked by intense thirst and heavy urination.
Diabetes insipidus occurs when the body can't regulate how it handles fluids. The condition is caused by a hormonal abnormality and isn't related to diabetes.